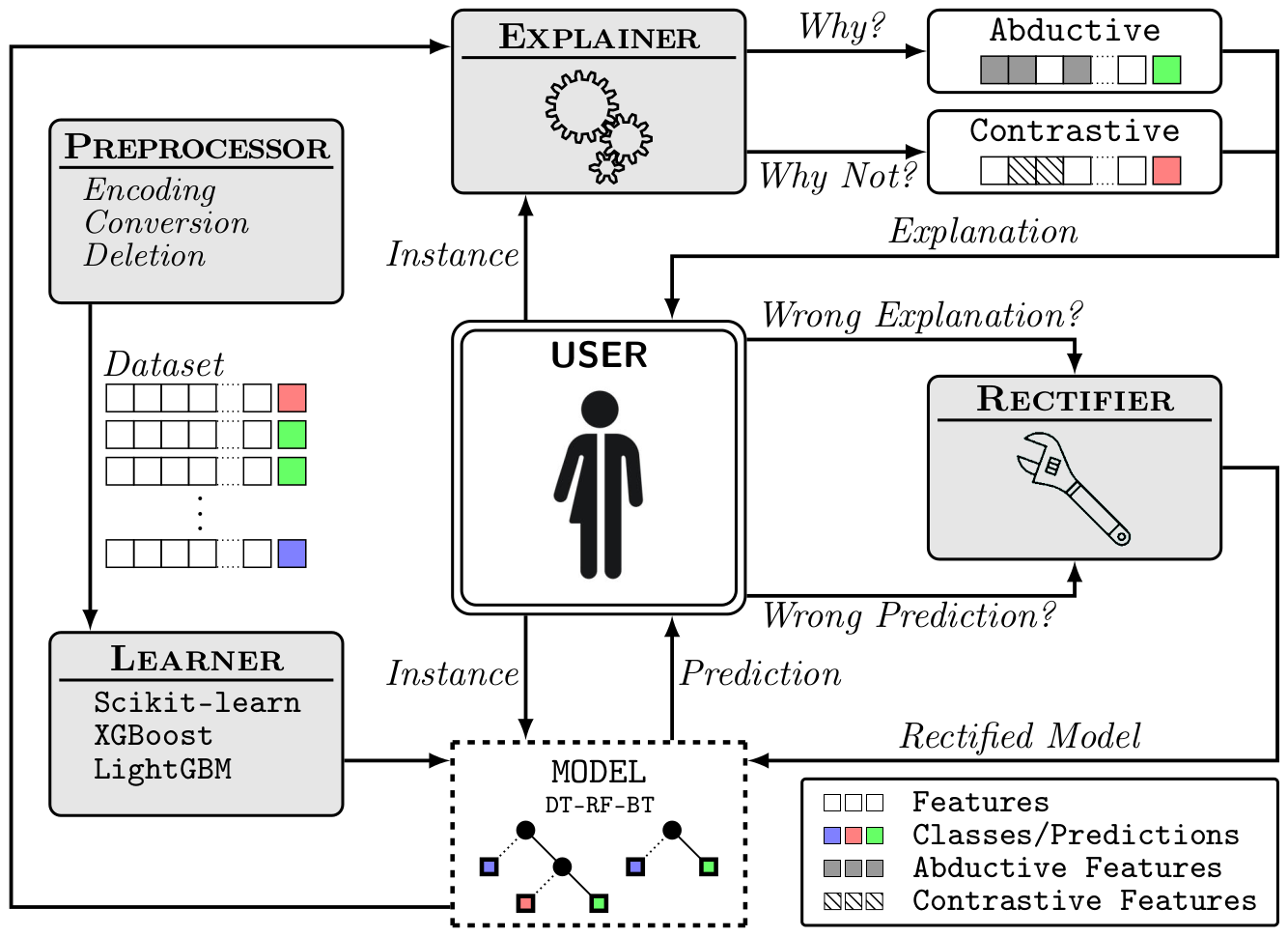
What is PyXAI?
PyXAI (Python eXplainable AI) is a Python library (version 3.6 or later) allowing to bring formal explanations suited to (regression or classification) tree-based ML models (Decision Trees, Random Forests, Boosted Trees, ...). PyXAI generates explanations that are post-hoc and local. In contrast to many popular approaches to XAI (SHAP, LIME, ...), PyXAI generates explanations that are also correct. Being correct (aka sound or faithful) indicates that the explanations that are provided actually reflect the exact behaviour of the model by guaranteeing certain properties about the explanations generated. They can be of several types:
- Abductive explanations for an instance $X$ are intended to explain why $X$ has been classified in the way it has been classified by the ML model (thus, addressing the “Why?” question). In the regression case, abductive explanations for $X$ are intended to explain why the regression value of $X$ belongs to a given interval.
- Contrastive explanations for $X$ are intended to explain why $X$ has not been classified by the ML model as the user expected it (thus, addressing the “Why not?” question).
PyXAI also includes algorithms for correcting tree-based models when their predictions conflict with pieces of user knowledge. This more tricky facet of XAI is seldom offered by existing XAI systems. When some domain knowledge is available and a prediction (or an explanation) contradicts it, the model must be corrected. Rectification is a principled approach for such a correction operation.
New features in version 1.1.0:
- Rectification for DT (Decision Tree) and RF (Random Forest) models dedicated to binary classification.
- Visualization displayed in a notebook or on screen, and now also for time series problems.
- Enhanced compatibility with Mac OS and Windows
New features in version 1.0.0:
- Regression for Boosted Trees with XGBoost or LightGBM
- Adding Theories (knowledge about the dataset)
- Easier Model import (automatic detection of model types)
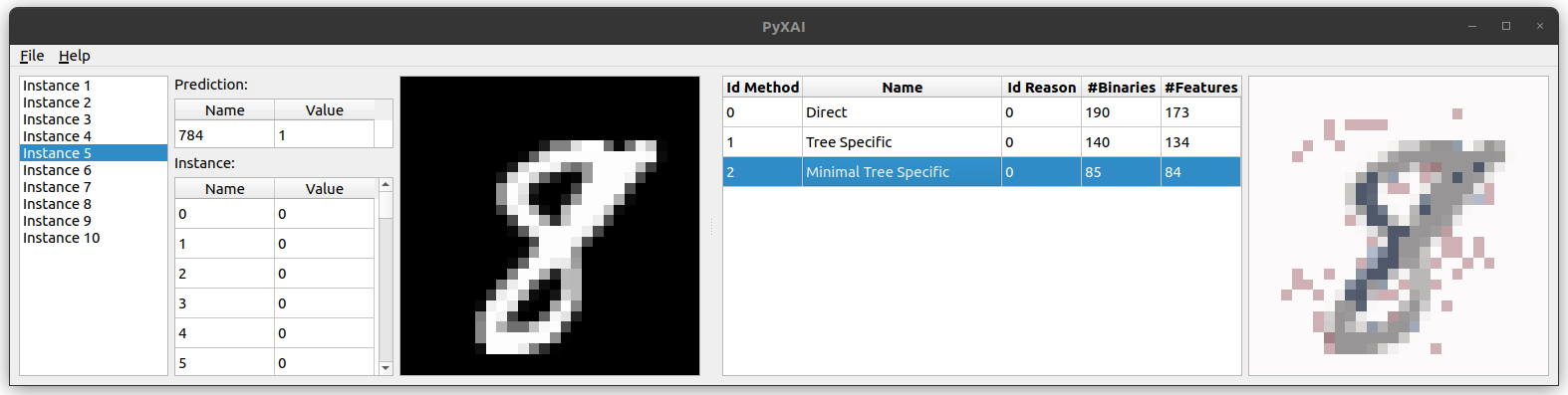
- PyXAI's Graphical User Interface (GUI): displaying, loading and saving explanations.
- Supports multiple image formats for image datasets
- Supports data pre-processing (tools for preparing and cleaning a dataset)
- Unit Tests with the unittest module
What is the difference between PyXAI and other methods?
The most popular approaches (SHAP, LIME, ...) to XAI are model-agnostic, but they do not offer any guarantees of rigor. A number of works by Marques-Silva and Huang, Ignatiev have highlighted several misconceptions about such approaches to XAI. Correctness is paramount when dealing with high-risk or sensitive applications, which is the type of applications that are targeted by PyXAI. When the correctness property is not satisfied, one can find ”counterexamples” for the explanations that are generated, i.e., pairs of instances sharing an explanation but leading to distinct predictions. Contrastingly, PyXAI algorithms rely on logic-based, model-precise approaches for computing explanations. Although formal explainability has a number of drawbacks, particularly in terms of the computational complexity of logical reasoning needed to derive explanations, steady progress has been made since its inception.
Which models can be explained with PyXAI?
Models are the resulting objects of an experimental ML protocol through a chosen cross-validation method (for example, the result of a training phase on a classifier). Importantly, in PyXAI, there is a complete separation between the learning phase and the explaining phase: you produce/load/save models, and you find explanations for some instances given such models. Currently, with PyXAI, you can use methods to find explanations suited to different ML models for classification or regression tasks:
- Decision Tree (DT)
- Random Forest (RF)
- Boosted Tree (Gradient boosting) (BT)
In addition to finding explanations, PyXAI also provides methods that perform operations (production, saving, loading) on models and instances. Currently, these methods are available for three ML libraries:
- Scikit-learn: a software machine learning library
- XGBoost: an optimized distributed gradient boosting library
- LightGBM: a gradient boosting framework that uses tree-based learning algorithms
It is also possible to leverage PyXAI to find explanations suited to models learned using other libraries.
What does this website offer?
In this website, you can find all what you need to know about PyXAI, with more than 10 Jupyter Notebooks, including:
- The installation guide and the quick start page
- About models:
- How to prepare and clean a dataset using the PyXAI preprocessor object?
- How to import a model, whatever its format? Importing Models
- How to generate a model using a ML cross-validation method? Generating Models
- How to build a model from trees directly built by the user? Building Models
- How to save and load models with the PyXAI learning module? Saving/Loading Models
- About explanations:
- The concepts used byt the PyXAI explainer module: Concepts
- Theories gathering pieces of knowledge about the dataset. PyXAI offers the possibility of encoding a theory when calculating explanations in order to avoid the computation of impossible explanations: Theories
- The PyXAI library offers the possibility to process user preferences (prefer some explanations to others or exclude some features): Preferences
- How to set a time limit? Time Limit
- How to compute explanations for classification tasks? Explaining Classification
- How to compute explanations for regression tasks? Explaining Regression
- About rectification:
- How to rectify a DT model? Rectification for Decision Tree
- How to rectify a RF model? Rectification for Random Forest
- About visualization:
- How to generate images to represent explanations (in a notebook or save them in png format)? Visualization of Explanations (Without GUI)?
- How to use the PyXAI's Graphical User Interface (GUI) for visualizing explanations?
How to use PyXAI?
Here is an example (it comes from the Quick Start page):
PyXAI in action
from pyxai import Learning, Explainer
learner = Learning.Scikitlearn("tests/iris.csv", learner_type=Learning.CLASSIFICATION)
model = learner.evaluate(method=Learning.HOLD_OUT, output=Learning.DT)
instance, prediction = learner.get_instances(model, n=1, correct=True, predictions=[0])
explainer = Explainer.initialize(model, instance)
print("instance:", instance)
print("binary representation:", explainer.binary_representation)
sufficient_reason = explainer.sufficient_reason(n=1)
print("sufficient_reason:", sufficient_reason)
print("to_features:", explainer.to_features(sufficient_reason))
instance, prediction = learner.get_instances(model, n=1, correct=False)
explainer.set_instance(instance)
contrastive_reason = explainer.contrastive_reason()
print("contrastive reason", contrastive_reason)
print("to_features:", explainer.to_features(contrastive_reason, contrastive=True))
explainer.visualisation.screen(instance, contrastive_reason, contrastive=True)
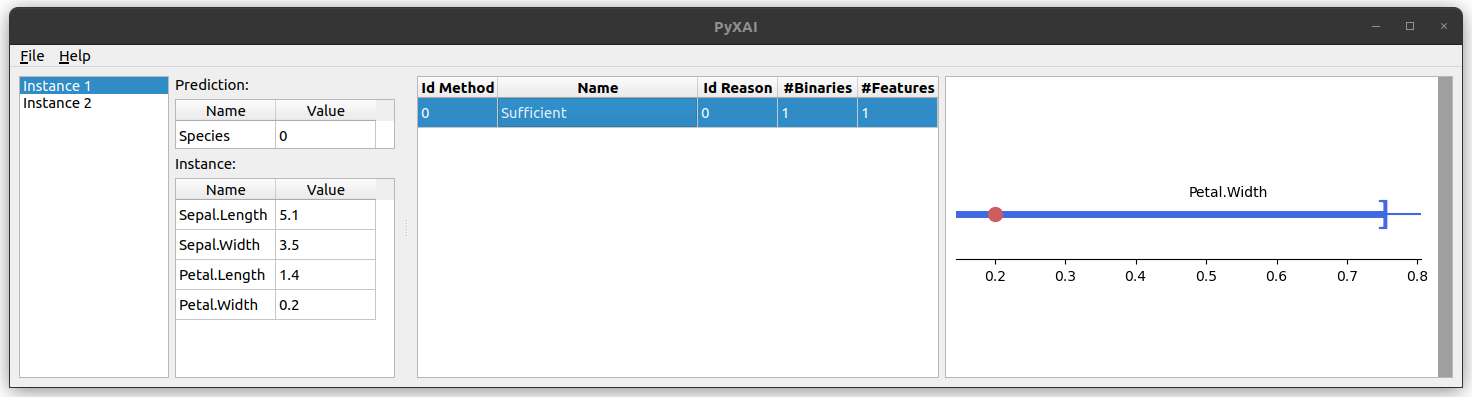
As illustrated by this example, with a few lines of code, PyXAI allows you to train a model, extract instances, and get explanations about the classifications made.



